
 by
Mamisoa Andriantafika
by
Mamisoa Andriantafika
Glaucoma is a common, insidious and potentially blinding disease.
Glaucoma is a disease affecting the optic nerve. It is made of fibers linking photoreceptors of retina to optic ways connected to regions of the brain processing the visual signals.
Main cause of glaucoma is a high ocular pressure inducing a loss of peripheral vision. At an advance stage, it can lead to blindness.
The natural flow of aqueous humor starts from the ciliary body behind the iris to end in the trabeculum between the iris and the cornea. A disturbance of this flow can lead to ocular hypertension and compression of the optic nerve.
Glaucoma is a common, insidious and potentially blinding disease.
Glaucoma is affecting about 3.5% of the population.
Optic fibers first suffer and then die progressively. This loss will lead to the observation by the eye docto of an excavation of the optic nerve, while the patient loose progressively his visual field.
Glaucoma is affecting about 3.5% of the population.
Open angle chronic glaucoma is the most prevalent type. The angle between the iris and cornea is open. Unbalance in the regulation of the aqueous humor can be caused by a perturbation from the source to the discharge route in the trabeculum. Ocular pressure is usually between 20 and 30mmHg and its evolution is progressive.
Angle closure glaucoma is a sudden event. The angle between the iris and cornea is narrow. In a situation where the pupil get dilated, the angle closes completely and the flow is blocked. Ocular pressure are very high, sometimes over 50mmHg. Evolution is rapid and if a treatment is not started early enough, the vision can be irremediably lost.
This glaucoma occurs more frequently in hyperopic persons where ocular structures are close be because of the shorter lenght of the eye. When the eye doctor screens a potential angle closure, he can decide to perform an preventive iridotomy with YAG laser.
Secondary glaucoma can be cause by a localized illness of the eye, for example a traumatism or toxicity linked to drops, or a general illness like a chronic ocular inflammation due to a systemic disease. Use of local corticoids, in the eye or inhaled, or taken by mouth are a non negligible cause of secondary glaucoma but also cataract. Therefore, the main treatment is the one of the cause underlying cause: stop the medication, if possible, or the treatement of the inflammation.
Congenital glaucoma is present since birth. It is usually detected during first years of life by the pediatrician and the eye doctor.
Corticoids can cause glaucoma.
Usually, patients have no symptom.
Usually, patients have no symptom. This is the main reason why a regular screening is advised after 40 years old.
When disease progresses, the patient will complain of subtle loss of contrast and peripheral vision. In the cas of angle closure glaucoma, symptoms are very acute: pain, headaches, vomiting and drastic loss of vision.
At an advanced stage, it can lead to blindness. The loss of optic fibers is at this time unrecoverable.
Other subtle are subtle like alteration of color vision. The medical screening remains the most efficient way to avoid progression to an advanced stage. Today, most open angle chronic glaucoma are treated efficiently.
A regular medical screening is advised after 40 years old.
The main measure for screening is a high ocular pressure, usually over 20mmHg. It is only a threshold. Some glaucoma occur at lower pressure while higher pressure sometimes do not evolve in glaucoma. Ocular pressure is not the only sign of glaucoma.
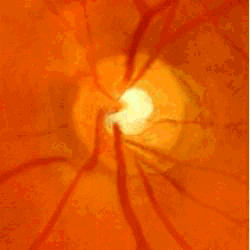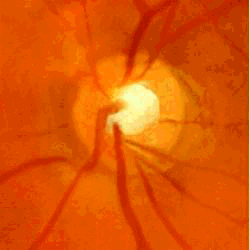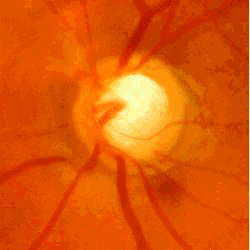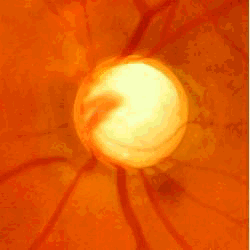
In the eye fundus, the eye doctor notices an excavation of the optic nerve which signs the loss of optic fibers. It can also be measured with an OCT scan.
Another very specific sign of glaucoma is an hemmorage near the border of the optic nerve. On the upper animation, one can see the progressive excavation, but also the occurence of the hemmorage.
When sufficient optic fibers are lost, visual field gets disturbed. In advanced stages, central vision can be affected and blindness can occur.
Ocular pressure, excavation of the optic nerve and visual field loss make the classic triade in glaucoma.
In the primary open angle glaucoma which is the most common, a medical treatment with drops instillation is usually enough to control the disease.
However, sometimes multiple trials with different drops and combinations are required to be efficient but also to get an acceptable local and general tolerance. As treatment is lifelong, tolerance is very important for the control of the disease.
Most of the time, treatment for glaucoma is lifelong.
SLT trabeculoplasty is an alternative to everyday drops instillation.
SLT trabeculoplasty can be an alternative to everyday drops instillation.
The patient has to be compliant: meaning he has to respect the posology and time of instillation, and continue this without forgetting. Indeed, alteration of optic fibers happens each time ocular pressure is too high, as so mainly when the effect of drops is gone.
Then a treatment that looks efficient as it is lowering enough the ocular can be inefficient in time as the disease continue to progresse. The eye doctor will face a paradoxal situation where the ocular pressure is low and the visual field continues to narrow.
When the medical treatment is not sufficient, other alternatives are available : different lasers with specific indications and surgery can be performed when all other medications have failed to control the glaucoma. All thoses treatments aim to balance the flow of the aqueous humor.
Surgery is indicated when medical treatment fails to provide progression of the disease.
In situation where irido-corneal angle is narrow, a preventive iridotomy can be performed.
In angle closure glaucoma condition, the treatment aims to decrease the pressure in emergency by performing a YAG laser iridotomy. A small peripheral aperture is made to facilite the flow through the iris and free the angle closure.
YAG laser iridotomy can also be performed preventively when a narrow angle is prone to close.